
Why Grip Strength Matters:
Grip strength serves as a significant marker of overall health and longevity. Research shows that weak grip strength in middle age is linked to increased risks of heart disease, cognitive decline, certain cancers, depression, disability, and even early mortality Grip Strength Longevity Clinicians are increasingly calling it a “vital sign” for aging—because stronger grips often correlate with longer, healthier lives.
To learn more: Grip strength can indicate health and longevity | CNN
How to Train:
- Deadhangs – Simply hanging from a pull-up bar for 30–60 seconds.
Farmer’s carries – Walking while holding heavy dumbbells or kettlebells engages support grip and builds full-arm strength.
Plate pinches, and wrist curls – Target pinch grip, and wrist/finger muscles.
Everyday load-bearing tasks – Activities like carrying groceries, using resistance bands, and performing pull-ups all enhance grip.
Tip: Consistency matters—perform several short sessions (e.g., 3–5 hangs or carries) multiple times weekly. Combine grip training with general strength work.

What it works: Medicine ball leg hold is primarily a core exercise, but it will also activate the quadriceps, glutes, hamstrings, and engages the hip flexors. There are numerous benefits with core strength, stability and lower body power, stability and balance. By adding the medicine ball, exercise becomes more challenging, which enhances these benefits further.
Event weight: 8Ib medicine ball (men) and 4Ib medicine ball (women).
Try out these Darebee workouts to help strengthen the lower abs and inner thighs.

What It Works: Wall sits are a powerful lower-body and core exercise. They target the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and abdominal muscles, helping you build strength and muscular endurance. Holding the position also works your back and pelvic muscles, improving core stability and posture. Over time, wall sits can help reduce knee and back pain, support better balance and coordination, and even assist with fat burning by increasing muscle mass and metabolism.
How to Train: Stand with your back flat against a wall, feet hip-width apart. Walk your feet forward and slide down until legs are at a 90° angle (like sitting in a chair). Tip: Place a foam roller across your thighs; if it rolls off, you’re not at a true 90°! Keep weight in your heels and hold for 5-60 seconds. Repeat 2-3 sets, increasing time as you get stronger.
9 Benefits of Wall Sits (and How To Do Them)
Check Out This: wall-sit-challenge.pdf, Wall Sit Workout - Fine Fit Day
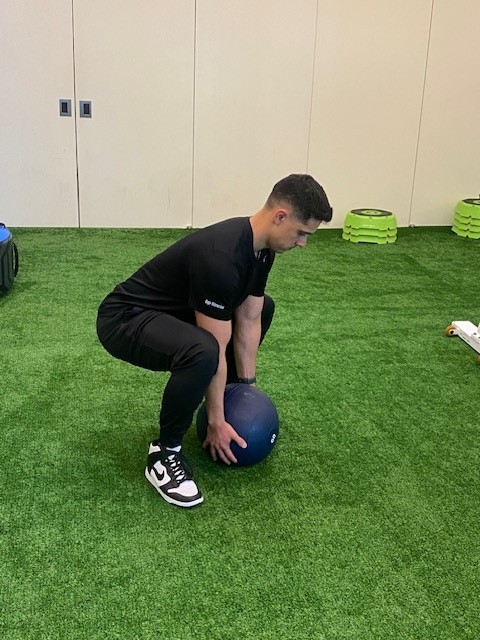


What it Works: It's a dynamic exercise that involves lifting and throwing the ball over the shoulder, utilizing muscles like the deltoids, trapezius, core stabilizers, quadriceps, glutes, and lower back muscles.
Event weights: 25lb slam ball for women, 40lb slam ball for men
How to Train: Practice event with weighted slam balls for time or reps. Vary the weights (heavier or lighter) to focus on speed or strength.
Check out this Darebee program which has a med-ball conditioning focus.
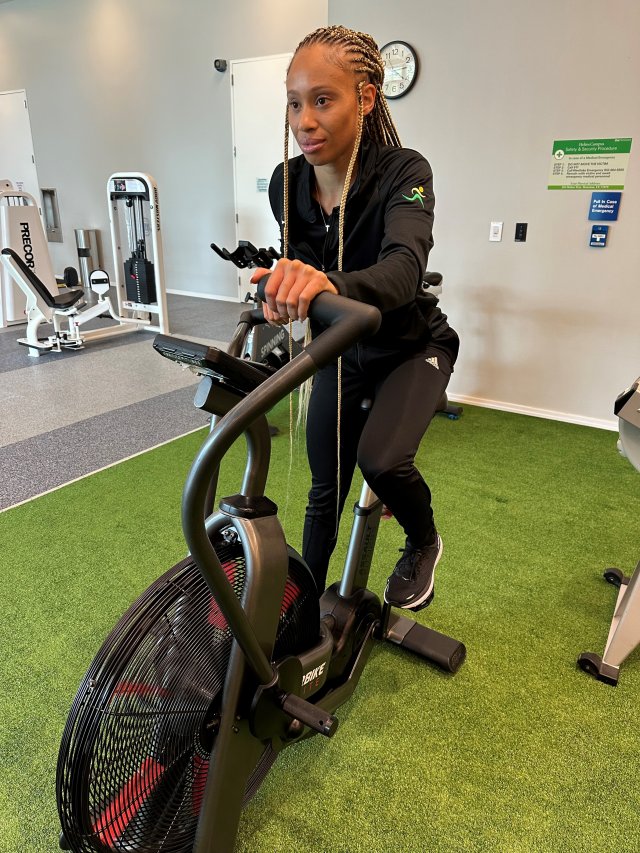

What it works: The air bike is primarily used for increasing cardiovascular endurance while improving functional fitness by utilizing synchronized movement throughout multiple muscle groups including the arms, back, core, and legs. It can be an excellent low-impact exercise that improves overall strength, muscle tone, and coordination alongside cardiovascular strength and stamina.
How to Train: Be sure to adjust the bike seat to around hip height, where your knees are slightly bent at the bottom of the pedal stroke. Engage your core and pedal with a forceful but smooth motion, avoiding swaying the upper body back and forth and maintaining an upright seated position.
Check out this article: How To Use an Air Bike: Tips, Technique & Benefits

What it works: This exercise targets your core and posterior chain (glutes, hamstrings, lower back, shoulders).
Benefits: Reduces muscle and joint pain. Can Help correct poor posture. Enhances balance and coordination.
How to Train: Start by sitting on the floor with your legs extended in front of you and palms on floor slightly behind and outside your hips. Lift your hips toward ceiling and straighten your arms and legs forming a straight line from head to heels. Squeeze core!
Check out this link to practice other variations to make it easier or more challenging: Reverse Plank: Exercises & Modifications
Why It Matters:
• Improves heart health, weight management, blood pressure, and insulin sensitivity.
• One mile runs boost VO₂ max, lower resting heart rate, strengthen bones, and enhance mood, focus, and sleep.
• Boosts mood, memory, balance, and immune function.
• Interval or “power” walking—like Japanese or Nordic walking—enhances calorie burn, endurance, and joint health.
How to Train: Run 3–4×/week with a mix of easy runs, interval/speed sessions, and strength/mobility training.
• Beginners can alternate run/walk (e.g., 2 min run + 1 min walk for 15–30 min) .
• Add tempo runs, hill repeats, form drills to boost pace and efficiency.

